Like the nostrils in our body which take incoming breath and emit outgoing breath, engine valves are part of the engine that controls the flow of the air and fuel in the vehicle.
Having a sound knowledge of engine valves will benefit you to maintain the engine valves in good condition. In this article, we will cover the basics of engine valves.
What is an engine valve and its function?
An engine valve is a crucial component within the internal combustion engine, ensuring the proper intake and exhaust flow in the cylinders. Here’s a simplified breakdown of its functions:
- Intake of Air-Fuel Mixture: Intake valves allow the air-fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber.
- Exhaust Gas Expulsion: Exhaust valves let out the burnt gases post-combustion.
- Maintaining Combustion Chamber Seal: When closed, valves seal the combustion chamber, ensuring compression and combustion phases occur effectively.
- Timing Control: Valves operate in precise timing with the piston movement, ensuring optimal engine performance.
In essence, engine valves play a pivotal role in managing the entry and exit of gases within the combustion chamber, directly impacting the engine’s performance and efficiency.
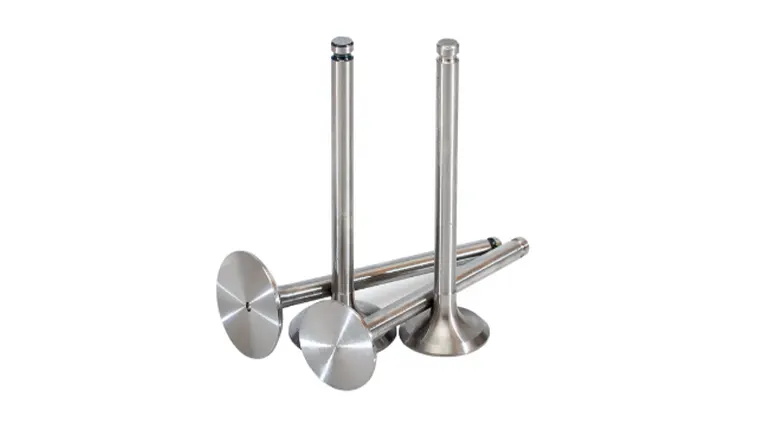

How do the engine valves work?
The intake and exhaust valves are designed to open and close at precise times without getting interfered with the other parts of the engine. It is called valve timing. The valve timing is controlled by the camshaft.
To understand the intake and exhaust process, let us explain the 4 combustion phases in a four-stroke engine.
- 1st stroke – The intake phase:
- Air and fuel are taken in through the intake valves in the cylinders. During the intake phase, the intake valves need to be opened and the exhaust valves should be closed.
- 2 & 3 Strokes – Combustion phase and Compression phase:
- When the intake valve is closed, the piston moves up the cylinder, and air is mixed with the fuel. Then the air and fuel mixture is compressed and then the spark plugs ignite them. At this time, all intake and exhaust valves need to be closed.
- 4th stroke – Exhaust phase:
- The burnt air and fuel are emitted through the cylinder. The During this time, only the exhaust valves need to be opened and the intake valves should remain closed.
Accordingly, the valves in the vehicle are very important in the control of the airflow of the engine.
How many valves does an engine have?
The number of valves in an engine can vary widely based on the engine’s design and purpose. A conventional four-stroke engine typically has at least two valves per cylinder – one intake and one exhaust.
However, modern engines often feature four valves per cylinder (two intake and two exhaust) to enhance performance, known as a multi-valve engine. Some high-performance or specialized engines might have more than four valves per cylinder to meet specific power and efficiency requirements. The exact number is determined by the engine’s design and intended use, with variations existing across different vehicle models and manufacturers.
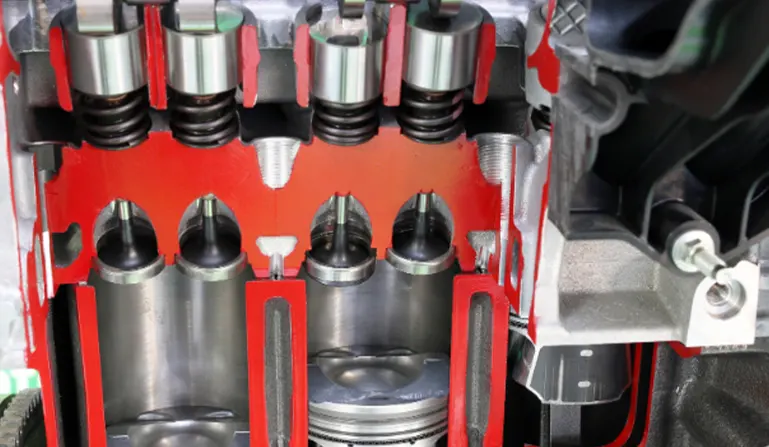
What are the different types of engine valves?
In a four-stroke engine, there are 2 valves, the intake valve, and the exhaust valve. On the other hand, in a multi-valve engine, there are 4 or 5 valves for the efficient performance of the engine as we discussed later.
Let us look at how the valves help the flow of the gas in the vehicle:
Intake valves: The intake valves allow air and fuel to enter the engine cylinder. The valve is made of two parts, the valve stem, and the valve head. The valve stem is made of hardened steel and the head is made of lightweight materials such as aluminum or titanium.
Exhaust valves: The exhaust valve emits burned gases from the engine cylinder. Unlike the intake valves, they are made of steel or iron to resist the temperature generated during the combustion process.
How to check for engine valve failures?
Engine valves are made to perform reliably and efficiently. However, there are a number of common issues that can arise over time.
- Bent valves: In an interference engine, the valves and the piston use the same space during the combustion process. When the valve is opened, the piston needs to be down and when the valve is up, the piston needs to be down. In case the valves get contacted with the pistons, the valve can bend.
- Burnt Valves: When the valve face is damaged by heat or corrosion, the valve will not seal properly. As a result, combustion gas escapes between the valve and valve seat. This can further damage the exhaust valves. A burnt valve can affect your vehicle’s fuel consumption and performance.
Tips on Maintenance of Engine Valves
Regular maintenance and proper care of engine valves are essential for ensuring efficient and reliable engine performance.
- Regular engine maintenance: Proper engine maintenance such as checking valve clearances and cleaning carbon deposits from the valve and cylinder head are essential during the recommended intervals.
- Engine valve adjustment: The gap between the valve lifter and the camshaft is called valve clearance. Over time, the valve clearance can go off from the specified range. To prevent this, you can make adjustments in the engine valve.
- Engine valve replacement: If the engine valve is damaged as a result of bending or burning, you need to replace it with a new valve.
In doing so, you need to remove the cylinder head, remove the damaged valve, and install a new valve.
Can I drive with bad engine valves?
Driving with bad engine valves is not recommended due to the critical role they play in ensuring optimal engine performance and vehicle safety. Compromised engine valves can lead to a plethora of issues, including reduced performance, misfires, compromised fuel efficiency, and potential engine damage. Here’s a closer look:
- Reduced Performance: Faulty valves can hinder the engine’s ability to breathe properly, affecting the power and responsiveness of the vehicle.
- Engine Misfires: Ineffective sealing or timing of the valves can lead to misfires, where the engine fails to run smoothly and might exhibit juddering or stalling.
- Decreased Fuel Efficiency: Impaired valves can disrupt the air-fuel mixture intake and exhaust gas expulsion, reducing the engine’s efficiency and increasing fuel consumption.
- Potential Engine Damage: Persistently driving with defective valves can lead to further engine damage, including burnt valves or damage to the pistons and cylinder walls.
while a vehicle might still be operable with faulty engine valves, it is unsafe and could lead to more severe engine damage in the long run. Immediate inspection and repair by a professional mechanic are advised to prevent further issues and ensure safe driving.
Conclusion
In conclusion, engine valves are a critical component of internal combustion engines and their proper functioning should not be overlooked.
By understanding the basics of engine valves, their design and operation, and the importance of proper maintenance and repair, you can help to keep your engine running smoothly and efficiently for years to come.

John Smith, a Los Angeles-based car specialist and automotive writer, boasts over 20 years in the industry. With a background as a master technician and a decade-long writing stint at notable automotive publications, John now shares his expansive knowledge on CarFinite, simplifying car maintenance for readers.

